New concept of Whole-process quality control
1.concept description
Quality Control is a general concept that can be applied in any field. For clinical laboratory medicine,Quality Control is the guarantee and premise to obtain true value,and to evaluate the precision, accuracy and stability of the whole test system.
2. why clinical medicine requires quality control:
(1)The traceability and precision of the test system.
(2)Accuracy of measurement results.
(3)Comparable results.
I. Raw Materials: our Beidou QDs system
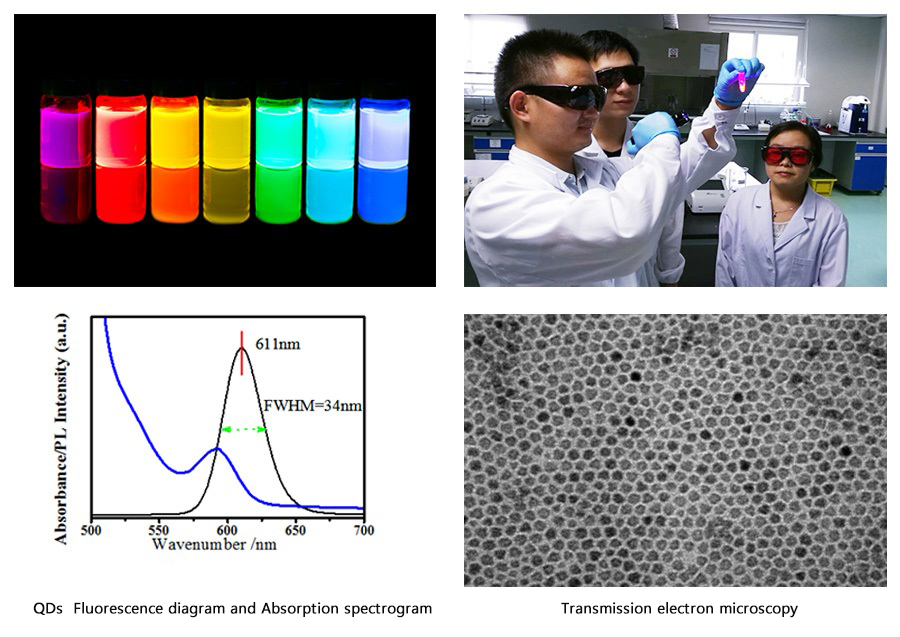
Description:
1.QDs Fluorescence diagram and Absorption spectrogram:
(1)FWHM:It is normally between 35nm and 38nm, and is less than 40nm. We can achieve 34nm with exclusive technology.
(2)Absorption peak:The fact that the first exciton peak of Absorption spectrogram(blue) be sharp will indicate a great uniformity of QDs.
2. Transmission electron microscopy:QDs have a great uniformity.
3. Our QDs:highly-productive raw material (5g QDs for 20 million reagent cards). The productivity and inter-batch variation of raw material are of great significance to the inter-batch variation and stability of reagents.
II.Production Quality Control:With the whole-process barcode inspection, poor-quality reagent strip/test card can be automatically identified and eliminated.The automatic equipment in replacement of manual full inspection can increase the accuracy and qualified rate of detection. All the manufacture process will conduct in accordance with the standards of ISO 13485 Medical devices -- Quality management systems -- Requirements for regulatory purposes.

III. Quality Control for analyzers :The patented Eu2+ & Mn2+ element quality control card employ absolute quantification method to assign values, which keeps the analyzer CV<1%.

Iv. Quality control of reagent R&D: self-developed freeze-dried powder quality controls (Levey-Jennings quality control)

| Number |
Controls |
Number of registration certificate |
| 1 |
降钙素原质控品(Procalcitonin(PCT)Control) |
粤械注准 20172400844 |
| 2 |
白介素6质控品(Interleukin-6(IL-6)Control) |
粤械注准 20172400852 |
| 3 |
C反应蛋白质控品(C-Reactive Rrotein(CRP)Control) |
粤械注准 20172400847 |
| 4 |
心肌肌钙蛋白 I 质控品(Cardiac Troponin I(cTnl)Control) |
粤械注准 20172400846 |
| 5 |
肌酸激酶同工酶质控品(Creatine kinase Isoenzyme-MB(CK-MB)Control) |
粤械注准 20172400849 |
| 6 |
D · 二聚体制控品(D-Dimer Control) |
粤械注准 20172400843 |
| 7 |
人心型脂肪酸结合蛋白质控品(Human Heart-type Fatty Aeid Binding Rrotein(H-FABP)Control) |
粤械注准 20172400851 |
| 8 |
肌红蛋白质控品(Myoglobin(MYO)Control) |
粤械注准 20172400848 |
| 9 |
N末端脑钠肱前体质控品(N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide(NT-proBNP)Control) |
粤械注准 20172400845 |
| 10 |
中性粒细胞明胶酶相关 脂质运载蛋白质控品(Neutrophil gelatinase-assoiated lipocalin(NGAL)Control) |
粤械注准 20172400850 |
Levey-Jennings control chart
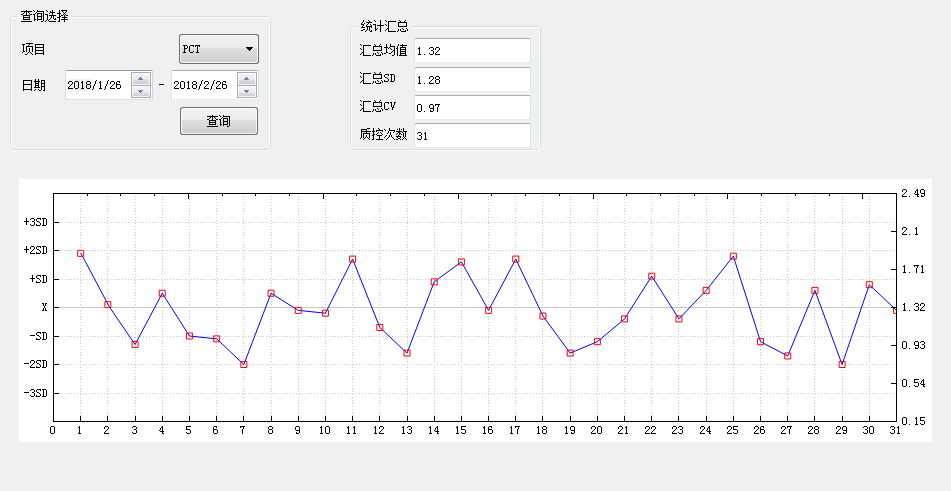
Description:
1.31 quality control test results are plotted in the chart. The quality control chart Have warning limit set as X+2SD and control limit set as X+3SD.
2.Levey-Jennings is the most commonly used control chart in laboratory . In general, the laboratory inspects the quality of the detection results by measuring the controls, and plots the quality control results on control chart. According to the control rules, the laboratory decides whether the detection is “in-control” or “out-of-control”.
3.We have the quality control conditions and strictly implement the international general quality control standards.
V. In clinical application: reading SD card for system calibration; the Control line used to eliminate abnormal reactions.

Description:
T line : Test line C line : Control line. In clinical application, the fluorescence intensity on Test line is directly proportional to sample concentration, so as to achieve quantitative detection. When the analyzers recognize the absence of Control line, the analyzers will classify the result to be invalid and do not calculate the measurement data, so as to eliminate abnormal reactions and ensure the accuracy of clinical test results.
Our core competencies
1.We are the first company in the world to bring QDs from academic research to clinical test.
2.We are the first company in the world to develop, produce and industrialize QDs diagnostic reagents.
3.We are the first domestic company to put forward and implement the concept of Whole-Process Quality Control.
4.We are the only company with peripheral blood registration certificate from CFDA(QDs Immunofluorescence chromatography).
5.We are the only company in the world with the exclusive patents for PCT/IL-6, PCT/ IL-6 /CRP combined detection.
6.We are the only company in the world achieve hs-cTnI assay with a LOD of 0.005ng/mL.